Squeezing your node on EKS for the money of it!
I dont know about you, but i dont think burning some reasonable amount of funds on under-utilized compute is fair, so it means i will queeze my compute for the money of it.
By default there is a limit/capped number of pods that can run on EKS Node(compute)
Like t4g.medium now, see the below screenshot, it can only allow 17 pods
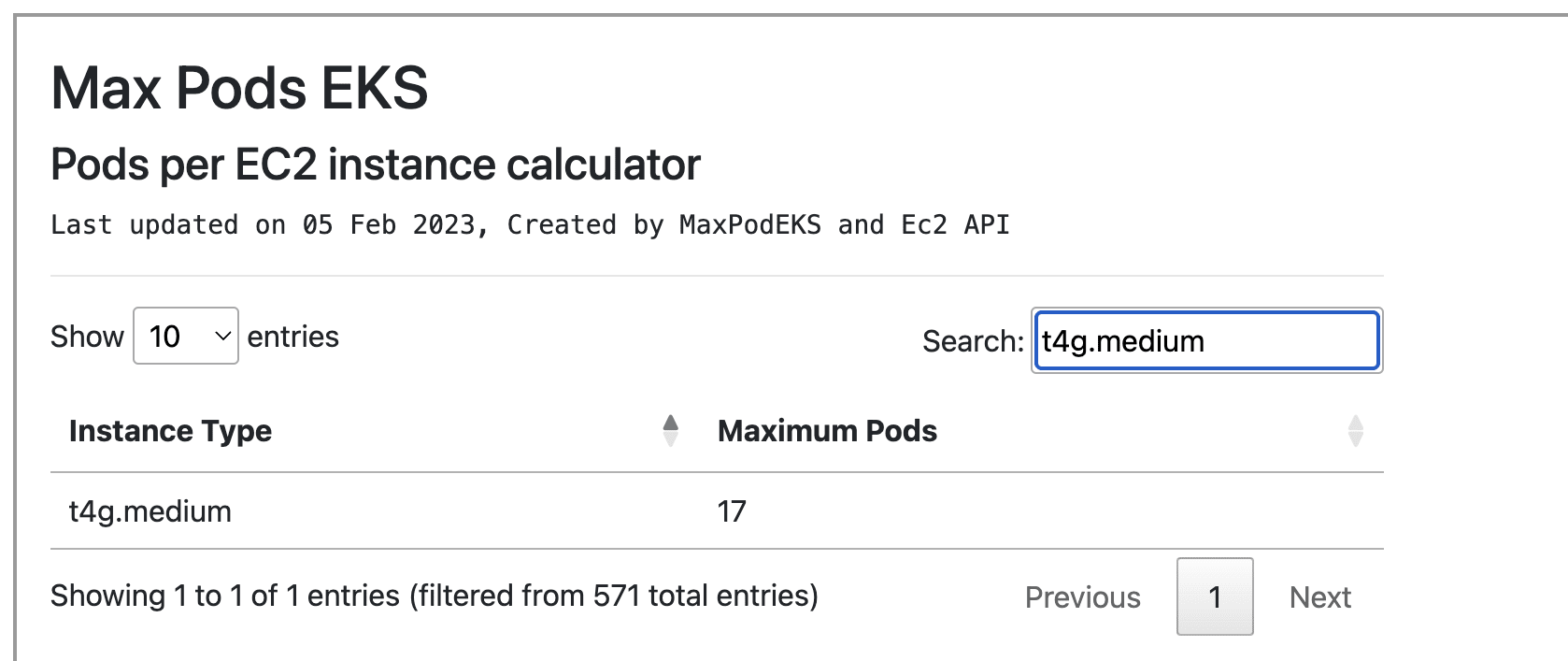
Default t4g.medium max-pods
17 Pods? core-dns is two pod, aws-node is one pod, kube-proxy is one pod, external-dns is one, aws alb or nginx ingress takes 2-3 pods, you need persistent storage, efs or ebs takes upto 3, 2 controller and 1 efs or ebs node, metric-server is one pod, karpenter or any other autoscaler takes two pods.
Now do the calculation, almost 14 pods already, and this is just pods we consider to be crucial or are dependencies, whats the allocation thats left? 3 pods.
Will the 3 pods left be okay for our main application? i bet not, it might be okay for you, but we have multiple services to deploy, there is still redis, kafka there and more.
The interesting part is, if the 17 pods space is filled, irrespective of wheather you have used up the resources, like the example i gave above t4g.medium is 2vCPU and 4GB Memory, you are then required to add more nodes if you want to add more pods to your EKS cluster.
And there you have a very underutilized compute (EKS Node) wasting away, because you sure are paying for the compute, more worst if its not a spot node.
You can easily check the maximum pod your instance(node) or compute can allow here maximum pod chekcer or use AWS MAX-POD Calculator or K8s Instance Calculator
So how do we resolve this?
Pod Density
Now that you know the maximum number of pods your node(compute) can run, you need to note that this limitation is determined by the number of Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs) and IP addresses per ENI supported by the instance type.
Now you need to modify the max-pod value in the EKS Node(compute) by altering the value either through custom AMI, user data script or Kubelet config.
I want to assume you provisioned your Elastic Kubernetes Cluster(EKS) with terraform or opentofu, and you are using a managed node groups with AL2023 ami type, if so the below cloudinit syntax will help modify the max-pod value for your instance, the maximum you can go is 110 to 250 pods depends on how big your instance is
managed_node_groups = {
regular = {
ami_type = "AL2023_x86_64_STANDARD"
desired_size = 10
min_size = 10
max_size = 20
instance_types = ["t4g.medium"]
capacity_type = "SPOT"
cloudinit_pre_nodeadm = [
{
content_type = "application/node.eks.aws"
content = <<-EOT
---
apiVersion: node.eks.aws/v1alpha1
kind: NodeConfig
spec:
kubelet:
config:
maxPods: 50
apiVersion: kubelet.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: KubeletConfiguration
EOT
}
]
}
After doing this, expect to run into IP exhaustion errors and more, you can read how you can increase the IP address allocation to solve the issue.
Also keep in mind that because you have 2vCPU and 4GB memory doesnt mean you will be able you use that up to, there is something called reserved memory and vcpu allocation in EKS, and your choice of maximizing your EKS Node(compute) also affect the allocation.
So lets say your t4g.medium can take 17 pods by default, here is what the reserved memory looks like
Reserved memory (17 pods) = 255Mi + 11MiB * 7 = 442MiB
Now if you increase it to 50 pods
Reserved memory (50 pods) = 255Mi + 11MiB * 50 = 805MiB
So your 2GB Memory (2048MiB) - 805MiB = 1243MiB compared to 2048MiB - 442MiB = 1606 MiB , you can read more about allocatable mememory and cpu in kubernetes nodes
Thats it folks 🤞🏽
Written with vibes and insha Allah from somewhere in this Rwanda traffic 😮💨